In the complex world of business, understanding the worth of a company is a critical aspect of decision-making. Business valuation services play a pivotal role in this regard. These services encompass a range of methodologies and techniques designed to determine the monetary value of a business. Whether it's for a potential sale, merger, acquisition, or simply to gain insights into its financial health, business valuation services provide essential information to stakeholders. In this article, we will explore the significance of business valuation services, the methods employed, and the scenarios in which they are indispensable. Alibaba.com
The Significance of Business Valuation Services
Business valuation services serve various purposes, each with its unique significance:
1. Transaction Support:
When buying or selling a business, it's crucial to establish a fair market value. Business valuation services provide an objective assessment that helps both parties negotiate a price that reflects the company's true worth. Sellers can use valuation results to justify their asking price, while buyers can ensure they are not overpaying.
2. Mergers and Acquisitions (M&A):
In M&A transactions, knowing the value of the target company is fundamental. Valuation services assist in assessing the synergy potential, identifying potential risks, and facilitating informed decision-making. Moreover, they aid in determining the exchange ratio in stock-for-stock transactions.
3. Estate Planning and Wealth Management:
For estate planning, it's essential to understand the value of business assets accurately. Business valuation services help individuals and families make informed decisions about estate taxes, succession planning, and wealth preservation.
4. Litigation and Dispute Resolution:
During legal disputes such as shareholder disputes, divorce settlements, or bankruptcy proceedings, business valuation services are indispensable. They provide expert opinions on the value of a business, which can significantly impact the outcome of the case.
5. Financial Reporting:
For financial reporting purposes, businesses may require the fair value assessment of their assets and liabilities. This is especially relevant for companies with complex financial structures or those following International Financial Reporting Standards (IFRS) or Generally Accepted Accounting Principles (GAAP).
6. Strategic Planning:
Understanding the value of your business is essential for strategic planning. It helps identify areas for improvement, assess the effectiveness of growth strategies, and make informed decisions about capital allocation.
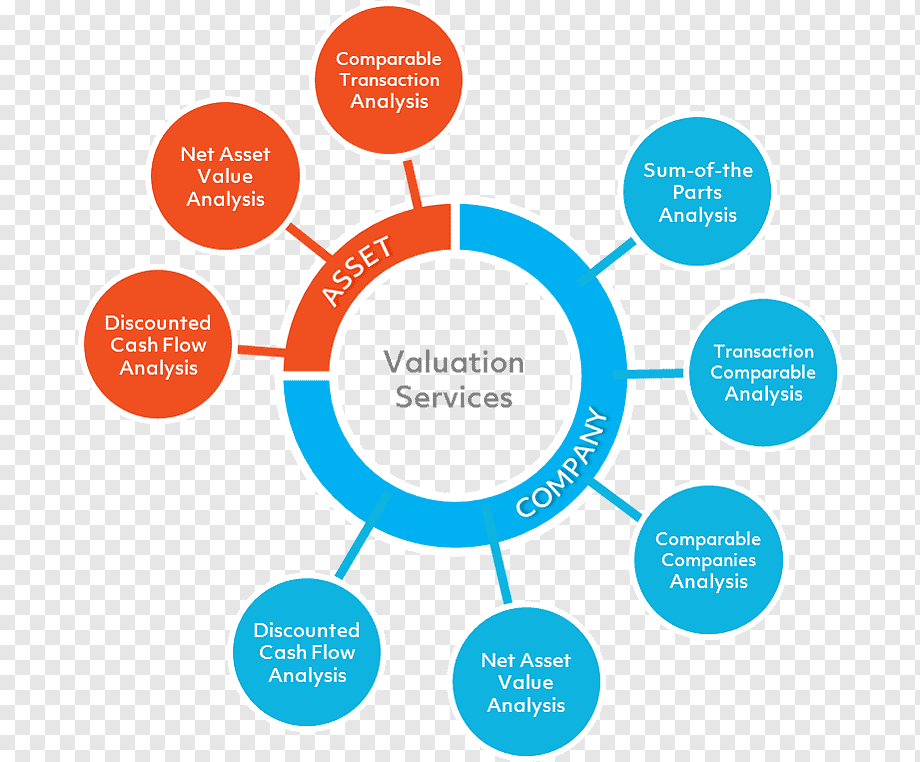
Business Valuation Methods
Business valuation services employ a variety of methods to assess a company's worth. The choice of method depends on the nature of the business, the industry it operates in, and the purpose of the valuation. Some common valuation methods include:
1. Income Approach:
This approach assesses the present value of future cash flows generated by the business. The Discounted Cash Flow (DCF) method is a commonly used income approach. It involves estimating the cash flows the business is expected to generate in the future and discounting them to their present value using a discount rate.
2. Market Approach:
The market approach compares the target business to similar businesses that have recently been sold. This method relies on market multiples such as Price-to-Earnings (P/E) ratios or Price-to-Sales (P/S) ratios to determine the valuation.
3. Asset Approach:
The asset approach focuses on the company's tangible and intangible assets. It assesses the net asset value of the business, which is the difference between its total assets and total liabilities. This approach is particularly useful for asset-intensive businesses.
4. Cost Approach:
The cost approach determines the value of a business by calculating the cost to recreate or replace its assets. This method is often used for businesses with unique assets or in industries where the value of assets is a significant driver of worth.
5. Comparable Company Analysis (CCA):
CCA involves comparing key financial metrics of the target business to those of publicly traded companies in the same industry. This method provides a relative valuation perspective and can help in understanding where the business stands in its competitive landscape.
6. Precedent Transaction Analysis:
Similar to CCA, precedent transaction analysis compares the target business to other businesses that have been acquired or sold in recent transactions. This method helps in determining what buyers have been willing to pay for similar companies.
Scenarios Requiring Business Valuation Services
Business valuation services are instrumental in various scenarios, some of which include:
1. Selling a Business:
Owners looking to sell their businesses need to establish an accurate selling price. A well-documented valuation report can attract potential buyers and expedite the sale process.
2. Buying a Business:
Buyers should perform due diligence before acquiring a business. Business valuation services help them assess whether the purchase aligns with their investment objectives and risk tolerance.
3. Estate and Tax Planning:
For estate planning and tax purposes, understanding the value of business assets is crucial. Accurate valuations can help minimize estate taxes and ensure a smooth transfer of assets to heirs.
4. Shareholder Disputes:
When disagreements arise among shareholders, determining the fair value of their ownership interests is essential. Business valuation services provide an objective assessment that can resolve disputes.
5. Financial Reporting:
Publicly traded companies often require fair value assessments for financial reporting, especially for complex assets or liabilities like derivatives or intangibles.
6. Divorce Proceedings:
In divorce cases involving business ownership, valuations can play a pivotal role in property division and alimony settlements.
7. Insurance Purposes:
Businesses may need to value their assets for insurance coverage purposes to ensure they have adequate coverage in case of disasters or unforeseen events.
8. Bankruptcy and Restructuring:
When a business faces financial distress or bankruptcy, determining the value of its assets is crucial for creditors and stakeholders involved in the restructuring process.
The Role of Valuation Professionals
Business valuation is a complex and specialized field that requires expertise and objectivity. Valuation professionals, such as Certified Valuation Analysts (CVAs) or Chartered Financial Analysts (CFAs), play a vital role in conducting valuations. Their responsibilities include:
1. Gathering Financial Information:
Valuation professionals collect and analyze financial statements, tax returns, and other relevant documents to understand the business's financial health.
2. Selecting Appropriate Valuation Methods:
Based on the purpose of the valuation and the characteristics of the business, professionals choose the most suitable valuation methods.
3. Performing Detailed Analysis:
They conduct in-depth analyses of financial data, market trends, and industry benchmarks to make accurate assessments.
4. Determining a Fair Value Range:
Valuation professionals often provide a range of values, reflecting different scenarios and assumptions. This helps stakeholders make informed decisions.
5. Documenting the Valuation Report:
A comprehensive valuation report is prepared, documenting the methodology used, assumptions made, and the resulting valuation.
6. Providing Expert Testimony:
In legal proceedings, valuation professionals may serve as expert witnesses to present their findings and defend their valuations.
Challenges in Business Valuation
Business valuation is not without its challenges and complexities. Some common challenges include:
1. Subjectivity:
Valuation often involves making subjective judgments, such as selecting appropriate discount rates or growth rates. Different analysts may arrive at slightly different valuations based on their assumptions.
2. Data Availability:
Accurate valuation relies on the availability of reliable financial data. Private companies may have limited financial disclosures, making valuation more challenging.
3. Market Volatility:
Market conditions can change rapidly, impacting the value of a business. Valuation professionals must account for these fluctuations.
4. Intangible Assets:
The growing importance of intangible assets, such as intellectual property or brand value, presents challenges in quantifying their worth accurately.
5. Legal and Regulatory Changes:
Changes in tax laws, accounting standards, or regulations can have a significant impact on business valuations.
Conclusion
Business valuation services are a cornerstone of sound financial decision-making. They provide a rational and objective assessment of a company's worth, helping stakeholders make informed choices in various situations, from mergers and acquisitions to estate planning and litigation. Valuation professionals play a critical role in this process, employing a range of methods and techniques to arrive at accurate and defensible valuations. While challenges and subjectivity exist in the field, the importance of business valuation services in the modern business landscape cannot be overstated. Whether you're a business owner, investor, or legal professional, a solid understanding of business valuation is essential for navigating the complexities of the corporate world. Visit official website grizzb.com