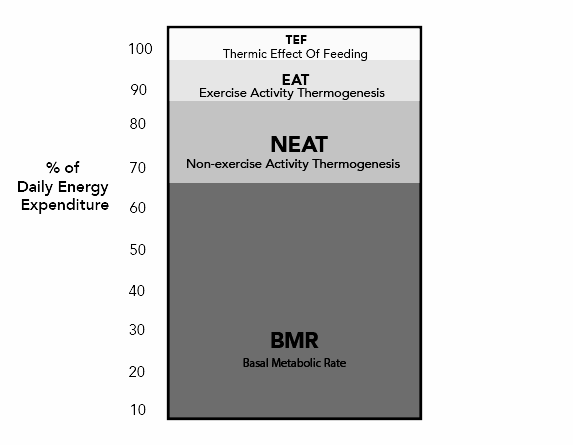
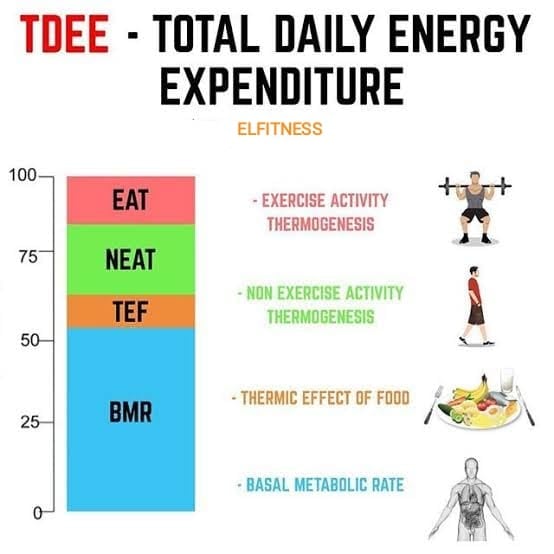
Total Daily Energy Expenditure (TDEE) is the total amount of energy or calories your body burns in a 24-hour period. It encompasses all the energy your body uses for various functions and activities throughout the day.
TDEE is composed of several components:
- Basal Metabolic Rate (BMR)
- BMR represents the energy your body needs to maintain essential life-sustaining functions like breathing, circulation, and brain function while at rest. It typically accounts for 60-75% of your TDEE.
- Physical Activity
- This includes both intentional exercise (Exercise Activity Thermogenesis or EAT) and non-exercise activity (Non-Exercise Activity Thermogenesis or NEAT). NEAT covers activities like walking, cleaning, and even fidgeting.
- Thermic Effect of Food (TEF)
- TEF is the energy required to digest, absorb, and metabolize the food you eat. It typically accounts for about 10% of your TDEE.
- Adaptive Thermogenesis (AT)
- AT refers to changes in energy expenditure in response to changes in energy balance, such as during periods of calorie restriction or overfeeding.
Your TDEE can vary based on factors such as:
- Age
- Sex
- Height and weight
- Body composition (particularly muscle mass)
- Activity level
- Genetics
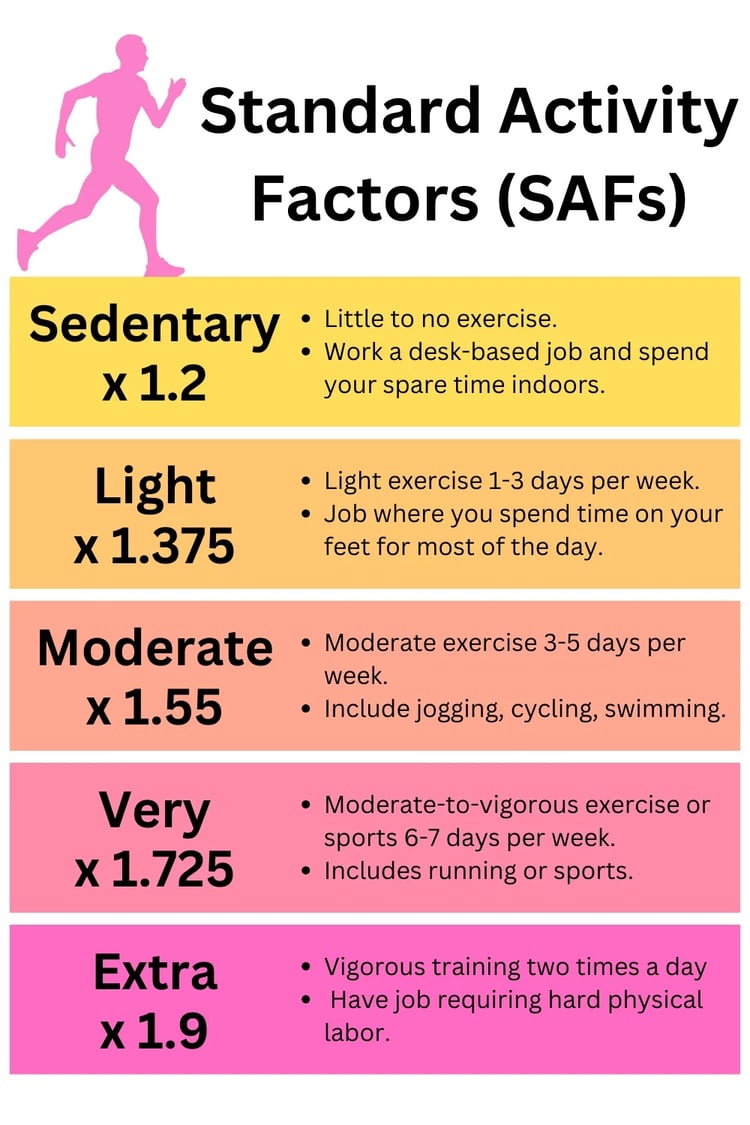
Understanding your TDEE is crucial for weight management. To lose weight, you need to create a calorie deficit by consuming fewer calories than your TDEE. To gain weight, you need to consume more calories than your TDEE.
TDEE can be estimated using various formulas that take into account your BMR and activity level. However, these estimates may not be accurate for everyone, especially those with certain medical conditions or the elderly.
What is TDEE and Why Does It Matter?
Total Daily Energy Expenditure (TDEE) is the total number of calories your body burns in a day. Understanding your TDEE is crucial for:
- Weight management: Knowing your TDEE helps you create effective meal plans for weight loss or gain.
- Fitness goals: Athletes and fitness enthusiasts can optimize their nutrition based on TDEE.
- Overall health: TDEE insights can improve your energy levels and metabolic health.
How Our TDEE Calculator Works
Our advanced TDEE calculator uses scientifically-backed formulas to provide accurate estimates. Here's what makes it stand out:
1. Multiple formulas: We use the Mifflin-St Jeor, Harris-Benedict, and Katch-McArdle equations for comprehensive results.
2. Customizable activity levels: From sedentary to extremely active, we account for various lifestyles.
Understanding Your TDEE Results
After using our calculator, you'll receive a breakdown of your energy expenditure:
- BMR: Basal Metabolic Rate - calories burned at rest
- TDEE: Total Daily Energy Expenditure - total calories burned per day
- Maintenance Calories: Calories needed to maintain current weight
- Weight Loss: Suggested calorie intake for gradual weight loss
- Weight Gain: Suggested calorie intake for muscle gain
TDEE and Weight Loss: What You Need to Know
Losing weight effectively isn't just about cutting calories. Learn how to use your TDEE to create a sustainable weight loss plan:
1. Create a moderate calorie deficit
2. Adjust your macronutrient balance
3. Incorporate strength training to preserve muscle mass
TDEE for Muscle Gain: Fueling Your Gains
Building muscle requires a strategic approach to nutrition. Discover how to leverage your TDEE for optimal muscle growth:
1. Calculate your surplus calories
2. Increase protein intake
3. Time your meals around workouts
How Activity Levels Affect Your TDEE
Your daily activities significantly impact your calorie burn. Explore how different lifestyles influence TDEE:
- Sedentary: Office workers, drivers
- Lightly Active: Teachers, retail workers
- Moderately Active: Construction workers, athletes
- Very Active: Professional athletes, manual laborers
TDEE and Hormones: The Hidden Connection
Hormonal imbalances can affect your TDEE. Learn about the interplay between hormones and metabolism:
1. Thyroid hormones and metabolic rate
2. Cortisol's impact on weight gain
3. How to optimize hormonal health for better TDEE
Tracking Your TDEE: Tools and Tips
Monitoring your TDEE over time can provide valuable insights. Discover the best methods for tracking:
1. Food diary apps
2. Fitness trackers and smartwatches
3. Regular weigh-ins and body measurements
TDEE Myths Debunked
Separate fact from fiction with our evidence-based approach to TDEE:
1. The starvation mode myth
2. Why eating more doesn't always boost metabolism
3. The truth about metabolic damage
By covering these topics comprehensively and providing valuable, actionable information, this content aims to attract organic traffic from people seeking to understand and utilize TDEE for their health and fitness goals.
The main differences between Basal Metabolic Rate (BMR) and Resting Metabolic Rate (RMR) are:
1. Measurement conditions:
- BMR is measured under more strict conditions, typically in the morning after 8-12 hours of fasting and sleep, with the person at complete rest.
- RMR is measured under less restrictive conditions, often including some recent low-effort daily activities.
2. Accuracy:
- BMR is considered a more accurate measure of the minimum energy required for basic life functions.
- RMR is slightly higher than BMR and more closely represents typical daily resting energy expenditure.
3. Calorie expenditure:
- BMR typically results in a slightly lower calorie expenditure estimate compared to RMR.
- RMR accounts for additional low-effort daily activities, resulting in a slightly higher calorie estimate.
4. Practical application:
- BMR is more commonly used in research settings due to its strict measurement requirements.
- RMR is more practical for everyday use and is often used in fitness and nutrition planning.
5. Measurement methods:
- BMR often requires overnight stays in a lab for accurate measurement.
- RMR can be estimated using equations or measured with less stringent protocols.
Despite these differences, BMR and RMR are often used interchangeably in practical settings, as they typically differ by only a small margin. For most people, RMR provides a sufficiently accurate estimate of their basal energy needs for daily life and fitness planning.