Patent Protection's Crucial Role in Innovation and Business
Innovation is the heartbeat of progress, and patents are the vital guardians of innovation. These legal instruments offer inventors and businesses the security and incentives they need to nurture groundbreaking ideas, develop new technologies, and transform industries. This article explores the pivotal role of patent protection in fostering innovation and driving the growth of businesses. We will journey through the various aspects of patents, their significance, and how they empower innovators to shape the world.
The Pillars of Innovation: Patents and Progress
At its core, innovation is about pushing the boundaries of what is possible, breaking through the constraints of the status quo, and exploring uncharted territories. Patents play a foundational role in this process by providing inventors with the assurance that their creative endeavors will be protected.
A patent is a legal document that grants its holder exclusive rights to an invention for a specified period, usually 20 years from the date of filing. In return for this exclusivity, inventors must disclose the details of their invention to the public, enriching the collective body of knowledge. This exchange of protection for disclosure lies at the heart of patent law and underscores its importance in encouraging innovation.
Patenting for Success: How Inventors and Businesses Benefit
Incentive for Innovation:
Patents serve as powerful incentives for inventors and businesses to invest in research and development. The promise of exclusive rights encourages individuals and organizations to channel their creativity into solving real-world problems and developing new solutions.
Knowledge Sharing:
Beyond protection, patents contribute to the dissemination of knowledge. Inventors must describe their inventions in detail, enabling others to build upon existing ideas and push the boundaries of innovation further. This sharing of knowledge fosters a culture of progress.
Economic Value:
Patents hold substantial economic value. They allow inventors and businesses to safeguard their intellectual property, gain a competitive edge in the market, attract investors, and generate revenue through licensing or selling their patents.
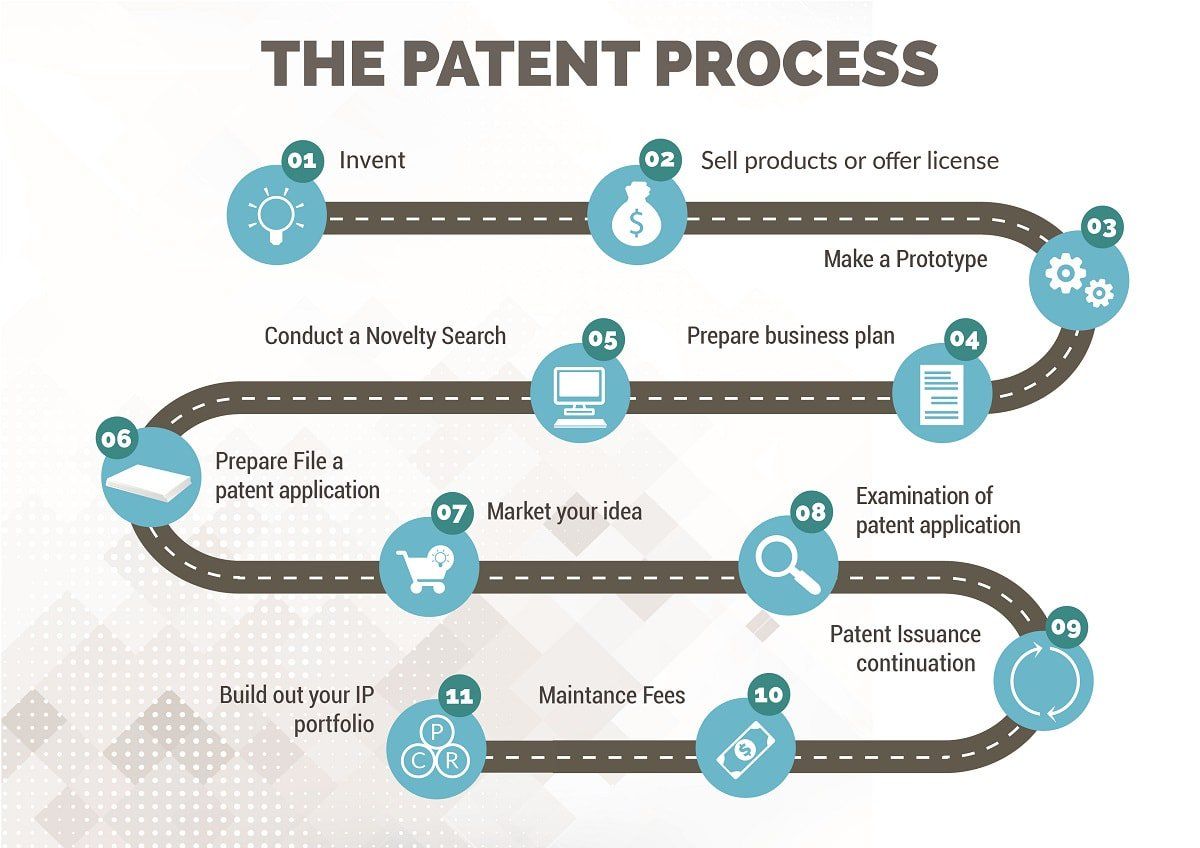
Navigating the Patent Landscape: From Idea to Intellectual Property
The journey from a spark of inspiration to securing a patent is a nuanced process that demands meticulous attention to detail. Here are the key steps:
Idea Development:
Innovation begins with an idea—a unique concept, a technological breakthrough, or a novel solution to an existing problem. This idea is the foundation upon which inventors build their innovations.
Patent Search:
Before proceeding, inventors must conduct a comprehensive patent search to ensure that their invention is genuinely novel. This search helps identify prior art that may impact the patentability of the idea.
Filing a Patent Application:
With a well-defined invention in hand, inventors prepare and submit a patent application to the relevant patent office. This application includes a detailed description of the invention, often accompanied by drawings or prototypes, as well as a set of claims defining the scope of protection sought.
Patent Examination:
The patent office meticulously examines the application, assessing whether the invention meets specific criteria, including novelty, non-obviousness, utility, and enablement. This examination process may involve interactions and clarifications between the inventor and patent examiners.
Publication and Grant:
Upon approval, the patent is granted, and the details of the invention are typically published, providing public notice of the patent's existence.
Maintenance and Enforcement:
To maintain a patent's validity, patent holders must pay required maintenance fees. Additionally, they have the legal right to enforce their patent rights by taking action against potential infringers.
Global Reach, Global Impact: The Significance of International Patents
In our interconnected world, inventions often transcend national borders. International patent systems like the Patent Cooperation Treaty (PCT) simplify the process of seeking patent protection across multiple countries. Under the PCT, inventors can file a single international patent application that is evaluated by various national or regional patent offices.
However, it's important to note that the PCT does not grant a single global patent; inventors must still file separate applications in individual countries or regions where they seek protection. This complex global landscape highlights the importance of securing innovation on an international scale.
Beyond Legal Documents: Patents as Drivers of Economic Growth
Patents are not mere legal documents; they are dynamic instruments that shape industries, drive economic growth, and enhance competitiveness. They differentiate businesses by offering unique products or services and act as barriers to entry, making it more challenging for competitors to replicate or imitate an invention.
In the business world, patents are often viewed as valuable assets. They can be monetized through licensing agreements or sold to generate revenue. Furthermore, having a robust patent portfolio can enhance a company's market position, attract investors, and create opportunities for collaboration and partnership.
Conclusion
Innovation is the engine of progress, and patents are the fuel that powers it. These legal instruments, born from the desire to protect and incentivize creativity, play an indispensable role in nurturing groundbreaking ideas, fostering knowledge sharing, and driving economic growth.
As inventors and businesses continue to push the boundaries of what's possible, patents will remain crucial tools, guiding them through the intricate journey from concept to intellectual property protection. In this ever-evolving landscape, patents empower individuals and organizations to shape the future and leave a lasting impact on our world.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Can I patent a business idea or a software program?
While it can be challenging to patent abstract ideas or software programs, specific software implementations or processes may be eligible for patent protection. The patentability of these concepts depends on various factors and may require consultation with a patent attorney.
How much does it cost to obtain a patent?
The cost of obtaining a patent varies based on factors such as the complexity of the invention, the type of patent, and the countries in which you seek protection. Fees include application filing fees, attorney fees, and maintenance fees over the life of the patent.
Can I publicly disclose my invention before filing a patent application?
Publicly disclosing your invention before filing a patent application can impact your ability to obtain a patent, as it may affect the novelty and patentability of the invention. It is generally advisable to consult with a patent attorney before making any public disclosures.
Do patents last forever?
No, patents have a limited duration. In most cases, utility patents last for 20 years from the date of filing, while design patents last for 15 years from the date of grant.
Can I sell or license my patent to others?
Yes, patent holders can sell or license their patents to others, allowing them to use or commercialize the patented invention in exchange for royalties or a lump-sum payment. This can be a way to monetize your intellectual property
