Internment of Japanese Americans (English)
On Sale
$5.00
$5.00
The internment of Japanese Americans in the United States during World War II
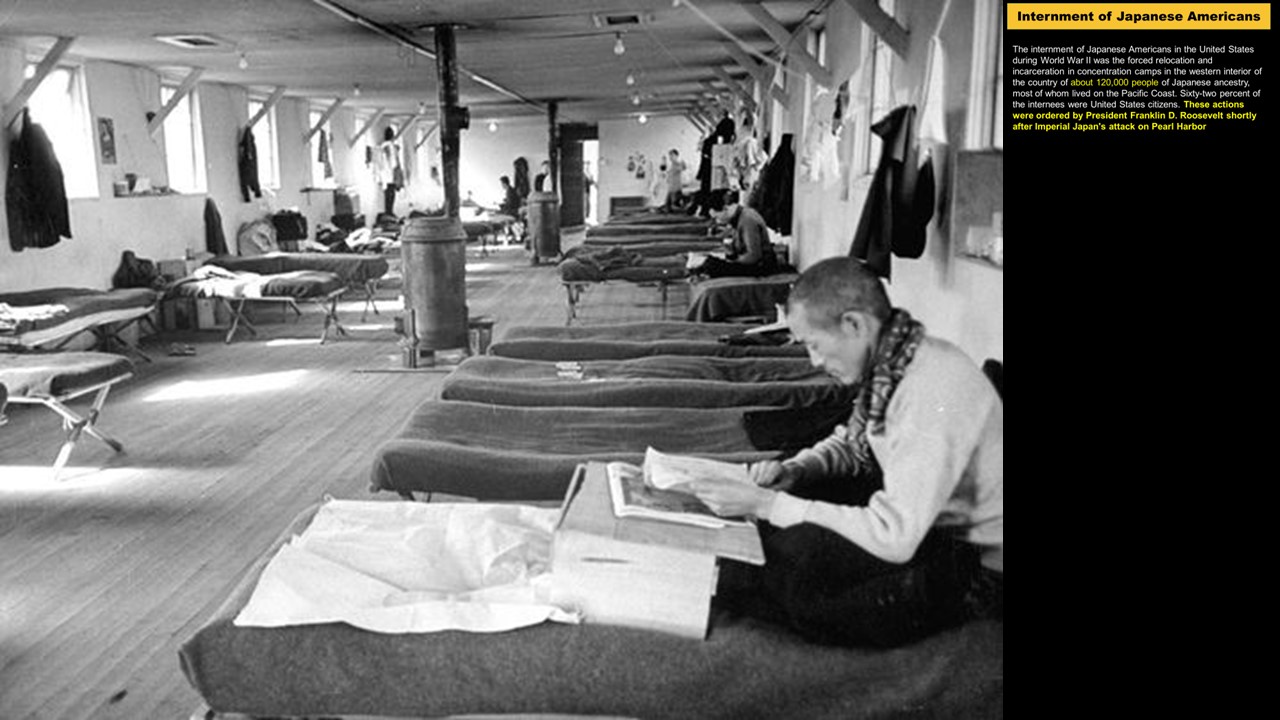
was the forced relocation and incarceration in concentration camps in the western interior of the country of about 120,000 people of Japanese ancestry, most of whom lived on the Pacific Coast. Sixty-two percent of the internees were United States citizens. These actions were ordered by President Franklin D. Roosevelt shortly after Imperial Japan's attack on Pearl Harbor
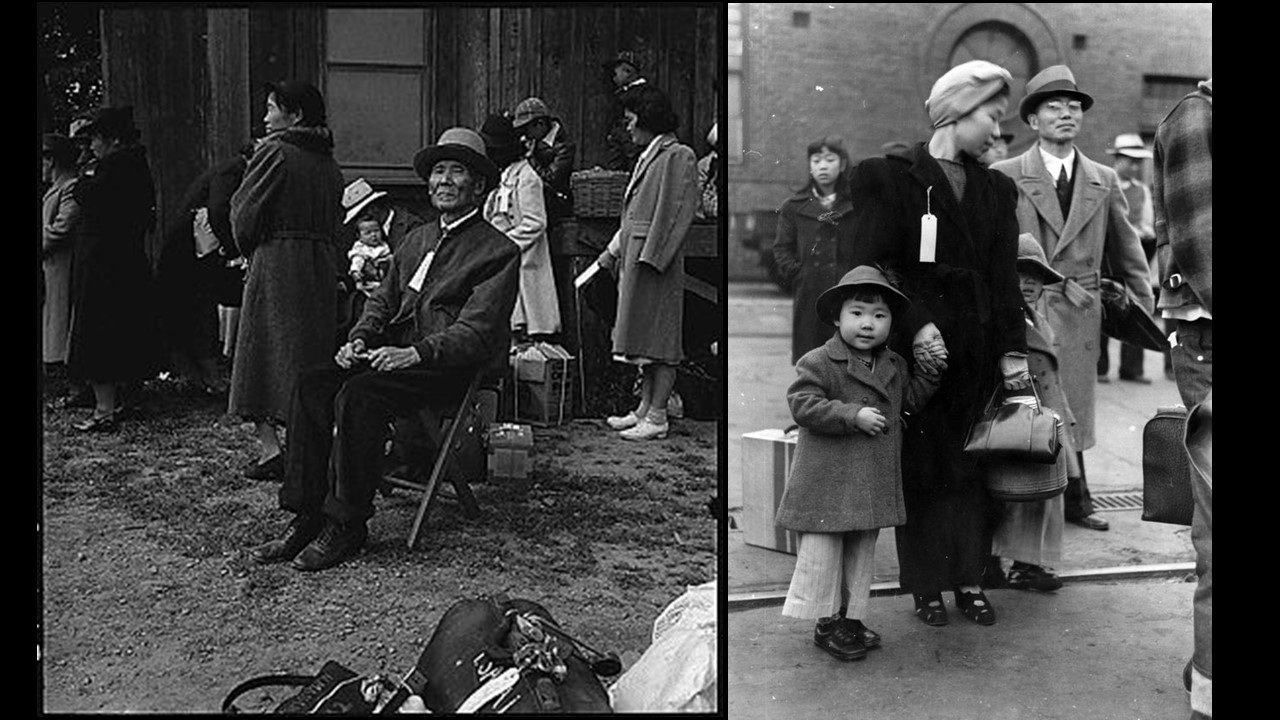
Of 127,000 Japanese Americans living in the continental United States at the time of the Pearl Harbor attack, 112,000 resided on the West Coast. About 80,000 were Nisei (literal translation: "second generation"; American-born Japanese with U.S. citizenship) and Sansei ("third generation"; the children of Nisei). The rest were Issei ("first generation") immigrants born in Japan who were ineligible for U.S. citizenship under U.S. law.
Japanese Americans were incarcerated based on local population concentrations and regional politics.
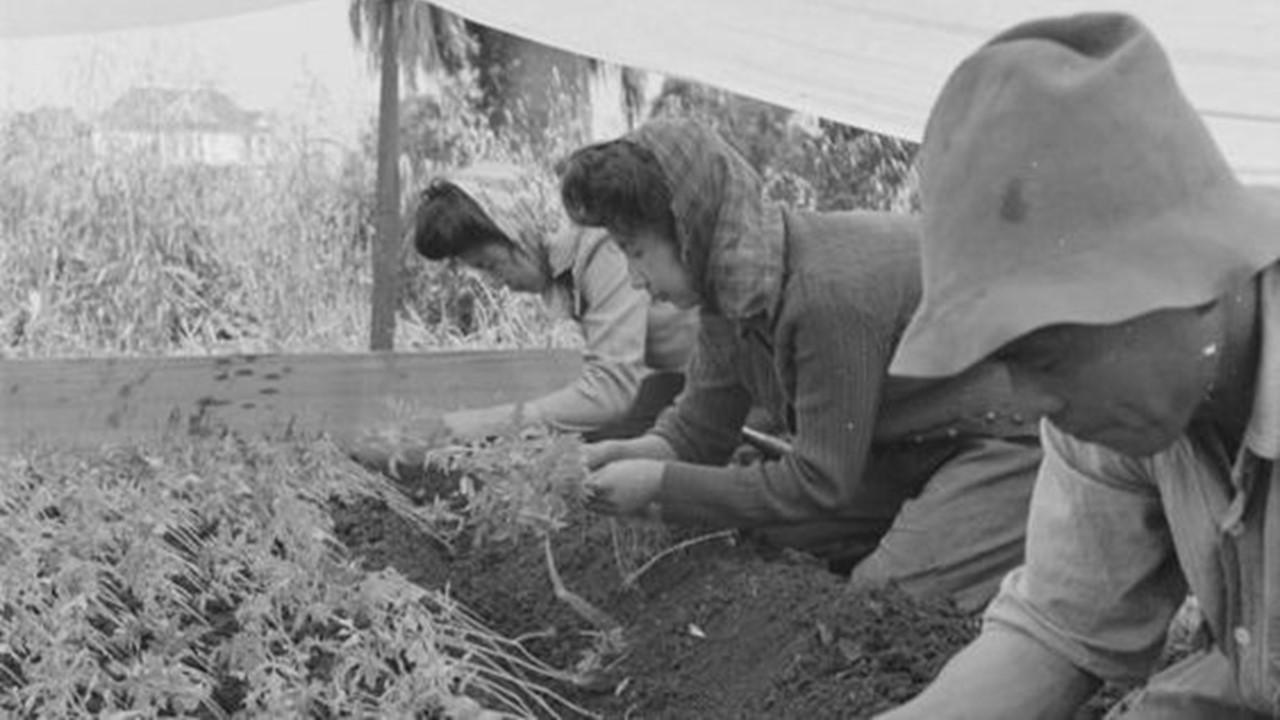
More than 112,000 Japanese Americans living on the West Coast were forced into interior camps. However, in Hawaii, where 150,000-plus Japanese Americans composed over one-third of the population, only 1,200 to 1,800 were also interned. The internment is considered to have resulted more from racism than from any security risk posed by Japanese Americans. California defined anyone with 1/16th or more Japanese lineage as sufficient to be interned. Colonel Karl Bendetsen, the architect behind the program, went so far as saying anyone with "one drop of Japanese blood" qualified.
In this slideshow (41) slideshow pages.
was the forced relocation and incarceration in concentration camps in the western interior of the country of about 120,000 people of Japanese ancestry, most of whom lived on the Pacific Coast. Sixty-two percent of the internees were United States citizens. These actions were ordered by President Franklin D. Roosevelt shortly after Imperial Japan's attack on Pearl Harbor
Of 127,000 Japanese Americans living in the continental United States at the time of the Pearl Harbor attack, 112,000 resided on the West Coast. About 80,000 were Nisei (literal translation: "second generation"; American-born Japanese with U.S. citizenship) and Sansei ("third generation"; the children of Nisei). The rest were Issei ("first generation") immigrants born in Japan who were ineligible for U.S. citizenship under U.S. law.
Japanese Americans were incarcerated based on local population concentrations and regional politics.
More than 112,000 Japanese Americans living on the West Coast were forced into interior camps. However, in Hawaii, where 150,000-plus Japanese Americans composed over one-third of the population, only 1,200 to 1,800 were also interned. The internment is considered to have resulted more from racism than from any security risk posed by Japanese Americans. California defined anyone with 1/16th or more Japanese lineage as sufficient to be interned. Colonel Karl Bendetsen, the architect behind the program, went so far as saying anyone with "one drop of Japanese blood" qualified.
In this slideshow (41) slideshow pages.