Information is the core of business today. Organizations are dependent on data systems to remain competitive, whether it is customer data, supply chain data, or financial data. Traditional databases like SQL and NoSQL solutions have over a decade,s been the foundation of digital infrastructure. But as blockchain technology emerges, the most pressing question business leaders are now asking is whether they should continue using databases that have proven to be effective or consider blockchain as a way of supporting their growing needs.
The decision is not as simple as it might appear. Traditional databases and blockchain have their own advantages, and they serve various business models and aims. To the decision-makers, the trick is to know how each system operates, what strengths it offers, and which alternative would be best suited to long-term objectives. This blog will discuss the differences, pros, cons, and practical applications of the two technologies to enable you to make an informed choice.
Good Read: 17+1 Top Blockchain Development Companies in 2025
Understanding Traditional Databases
Business applications have been based on traditional databases. They are relational databases, such as MySQL and Oracle, and non-relational databases, such as MongoDB. They are mainly used to store, organize and handle data effectively. They are mature, stable, and businesses trust them since they can process large amounts of data and maintain performance and reliability.
In a traditional database, information is managed by a single authority- your business or service provider. This centralization enables quicker queries, easier maintenance and more control. Nevertheless, it also implies one point of failure. In case the database is lost, corrupted, or hacked, then the whole system may be compromised. In most of the applications, particularly those that are internal to the business, this risk can be handled and is superseded by the efficiency and cost-effectiveness of traditional systems.
What Makes Blockchain Different
Blockchain is not another database- it is a decentralized ledger. In contrast to the traditional systems that have a single central authority, blockchain spreads data across several nodes. Every record is time-stamped, unchangeable, and encrypted with cryptography. This renders it almost impossible to make changes without agreement, guaranteeing data integrity and credibility among the participants.
Blockchain is especially helpful in situations when transparency, security, and decentralization are essential. Finance, healthcare, and supply chain management are some of the industries that are considering the use of blockchain since it has the potential to provide accountability among various stakeholders. Although it might not necessarily be the most effective in processing huge, real-time queries, blockchain is highly effective in a setting where trust and security are an absolute requirement.
Key Differences Between Blockchain and Traditional Databases
Centralization vs. decentralization is the most important distinction. Traditional databases provide businesses with full control, and this makes it faster and more convenient in their day-to-day operation. Contrastingly, blockchain disperses authority, minimizing the chances of manipulation, but in most cases, compromising speed and efficiency.
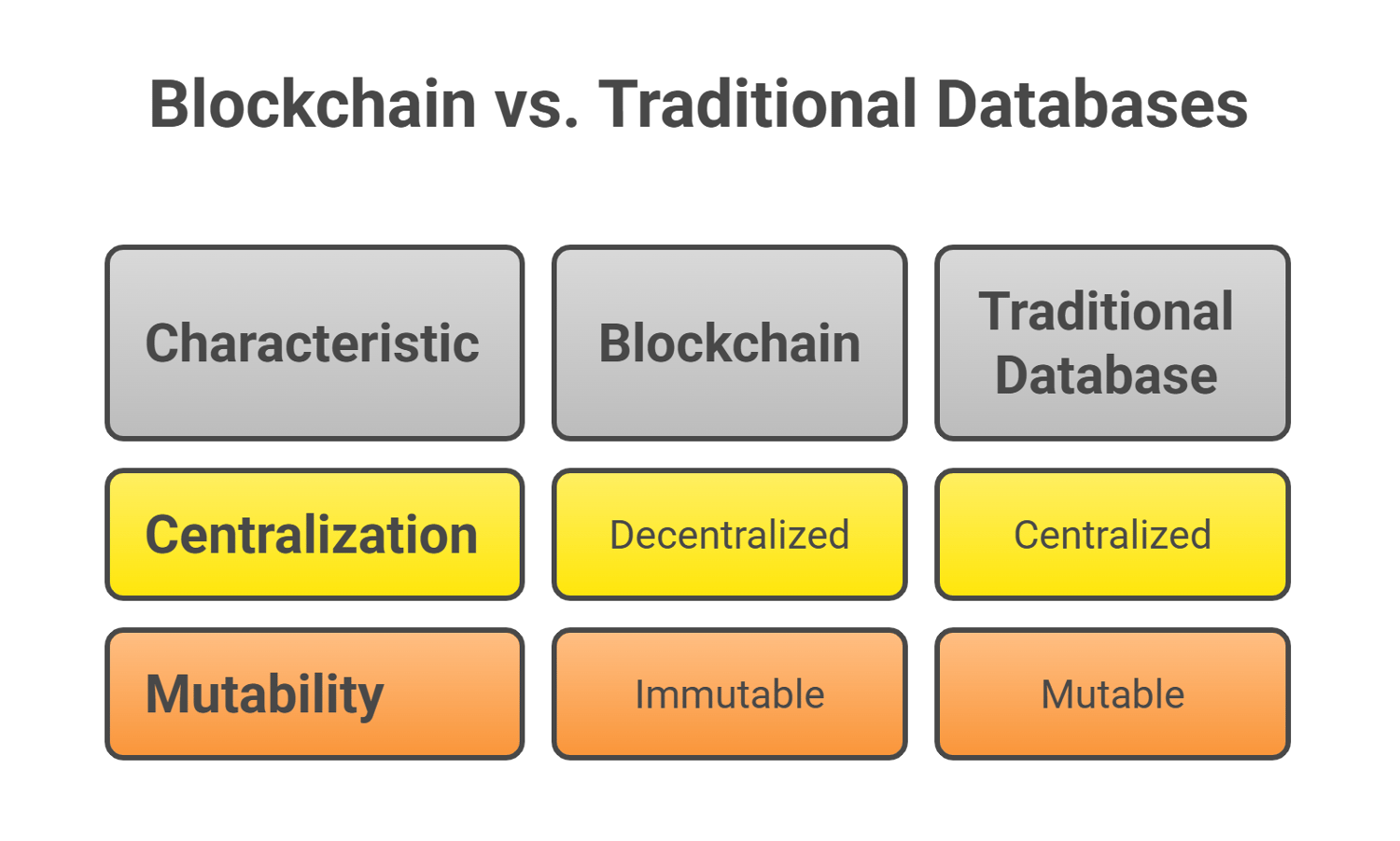
Mutability is another difference. Customary databases enable updating, editing or deleting of data. Although this is convenient, it opens up possibilities of manipulation or errors. The immutability of blockchain, however, means that once information is stored, it cannot be modified--making it a perfect fit in an application that needs records that cannot be altered, like a financial transaction or a legal contract.
When to Choose Traditional Databases
Conventional databases are still the preferred option to businesses that value speed, scalability, and cost-effectiveness. The best examples of where relational or NoSQL databases can shine are e-commerce sites, CRM systems and ERP platforms. They achieve high query volumes at low latency and are suitable for customer-facing and operational applications.
Unless your business model needs decentralized trust or cryptographic security, you do not have a pressing reason to use blockchain. As a matter of fact, the decision to use blockchain in such scenarios might needlessly complicate the work and raise expenses. The traditional databases are stable, broadly supported, and are continuing to adapt to the current needs with cloud-native and distributed models.
When Blockchain Becomes the Better Option
Blockchain is bright in the sphere where data integrity and transparency among various parties matter. The example of supply chain management is a classic one-blockchain that can track goods between a manufacturer and a retailer, and authenticity can be ensured in each step. Likewise, in finance, blockchain facilitates safe peer-to-peer transactions, which do not involve middlemen, saving money and time.
The other good use case is in smart contracts, where contracts are automatically run after specific, predefined conditions are achieved. In businesses that seek such applications, it is possible to work with a Smart Contract Development Company so that solutions can be tailored to your requirements. Blockchain may not be able to substitute the traditional databases in all processes, yet in the realms where trust, security, and automation count the most, it provides unparalleled value.
Evaluating Pros and Cons
To simplify the comparison, here’s a quick look at the strengths and limitations of both systems:
Traditional Databases
- Pros: High speed, cost-effective, mature technology, easy maintenance
- Cons: Centralized, vulnerable to tampering, limited transparency
Blockchain
- Pros: Decentralized, secure, immutable records, transparent transactions
- Cons: Slower performance, higher costs, complex implementation
This balance shows why businesses often choose hybrid approaches—leveraging traditional databases for operational needs while exploring blockchain for security and trust-focused use cases.
Hybrid Solutions: Best of Both Worlds
The best alternative to many businesses may not be making a decision between the two but a combination of the two. Day-to-day operations can be handled by traditional databases, whereas more important transactions or records, which need transparency and immutability, can be handled by blockchain. This is a hybrid model that enables businesses to find a balance between efficiency and trust.
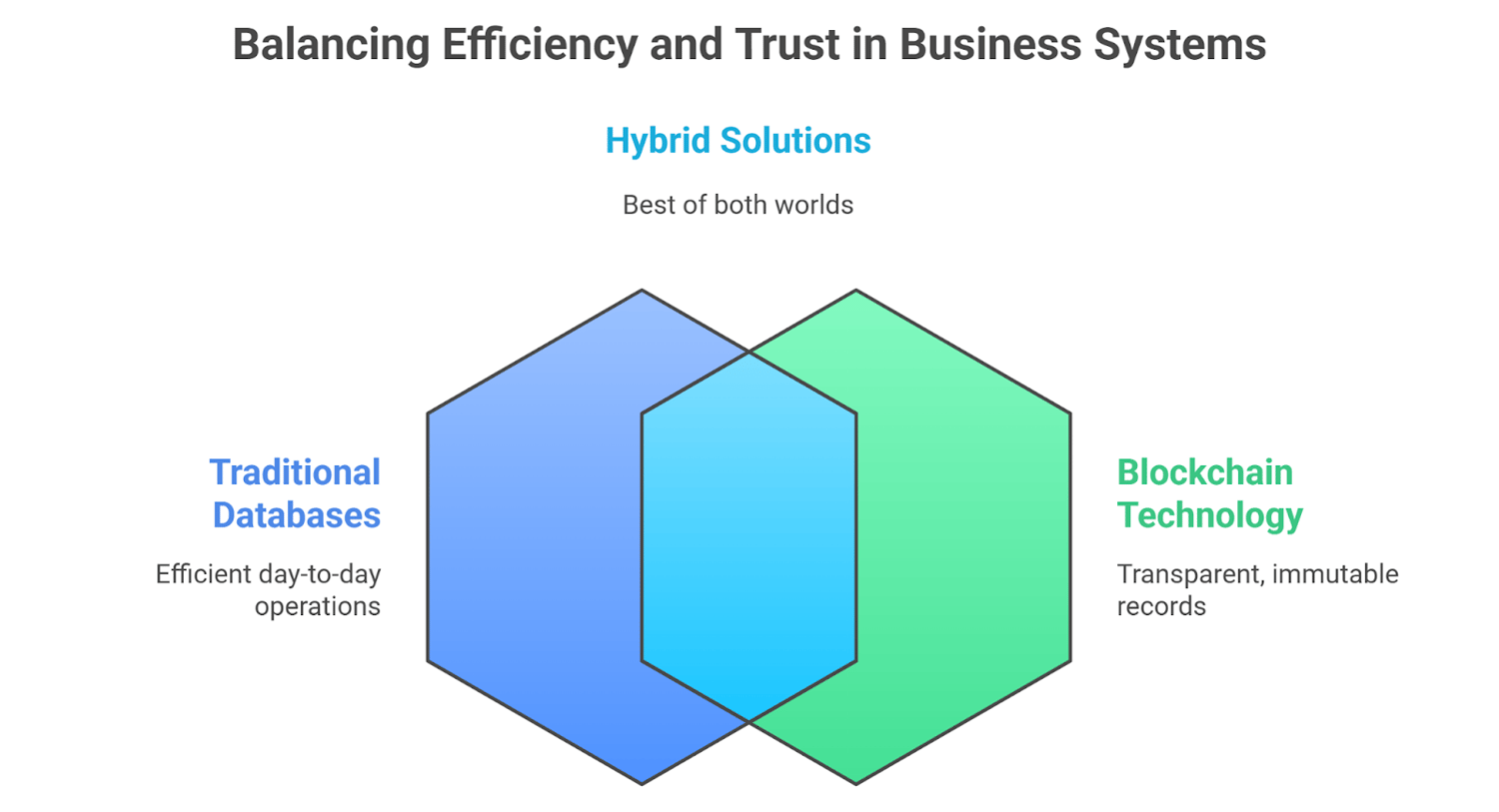
As an example, an inventory management database could be used by a logistics company, but shipment verification and tracking could be done with blockchain. This twofold strategy guarantees efficiency in operations without affecting authenticity and accountability among the stakeholders. Decision-makers need to consider whether a hybrid system of this nature can support their technical and strategic objectives.
Working With the Right Partner
The application of blockchain requires a specialized skill that transcends conventional IT skills. Companies can hire the services of a Blockchain Development Company to develop, create, and implement blockchain solutions that meet their specific needs. The correct partner will be able to assist in assessing whether blockchain actually contributes to your business model or whether a conventional database will be more effective.
In some cases, you may even have to hire blockchain developer resources directly on long-term projects. Experienced blockchain developers can assist in the seamless integration of blockchain solutions into your existing systems so that your business reaps the rewards of decentralization without interfering with the existing workflows.
The Future of Business Data Management
Blockchain versus traditional databases is not a contest of substituting one with the other but a matter of finding the right tool for the right job. The traditional databases will remain dominant where speed and simplicity are needed, and the use of blockchains will increase in industries where trust, automation, and security are the most important factors.
With the continued experimentation of decentralized applications and Web3 by more businesses, blockchain will be used more and more to supplement, but not to substitute, existing systems. Flexible decision-makers who are open to hybrid solutions and are in tune with expert collaborators will be in the best position to take advantage of the strengths of both technologies.
Final Thoughts
Blockchain and traditional databases are not a matter of technology hype but a matter of business strategy. Traditional databases are still the practical option in case you need speed, affordability, and centralised control. However, when your objectives are transparency, immutability, or multi-party trust, blockchain may be the game-changer you are looking for.
The best strategy most businesses can adopt is to consider the use cases where blockchain can help and develop hybrid frameworks that can exploit both systems. When you have the right partners, your organization will be in a position to use data systems not only as storage devices, but as sources of innovation and growth.