CONCRETE TECHNOLOGY & Structural analysis QUESTIONS:
1- Purpose of concrete curing:
To avoid the evaporation of the water from concrete and to keep moisture inside to
maintain the durability of the concrete
2- What is concrete workability:
The ease of fresh concrete which can be Mixed, placed, and compacted fully over the
formwork
3- What is the core test of concrete and when it is applied?
Core test is a destructive test done for concrete after 28 days usually done if there is any doubt of the compressive strength of concrete
4- What is the density of water?
1000 kg/m3
5- Why are admixtures added to the concrete?
To increase the durability & strength of concrete and some time for increasing the
workability
6- When we remove the shutter of columns?
After minimum 2 days
7- When we remove the shutter of sides beam or foundation?
It can be removed after 1 day
8- When we remove the shutter of normal slab?
After minimum 14 days
9- How many cubes required for 110 m3 of concrete in one day?
Total of 9 cubes: 3 to do compressive strength after 7 days
3 after 28 days
3 extra cubes
10- Definition of hydration:
It is the reaction between water and cement
11- What is the length of the CG of compression and CG of a tension member?
Effective depth
12- Definition of water cement ratio:
Weight of water over the weight of Cementous components or cement
13- What is the minimum thickness of a structural member?
15 cm
14- Techniques used for beam repair.
Steel plate; carbo fiber cover; fiber road; shipping, cleaning of steel and casting microconcrete high strength
15- Most used of slabs.
a- Hollow slab
b- Solid slab
c- Post tension slab
d- Flat slab
e- Prestressed slab
16- When is shotcrete used?
a- Difficulty of placing a shutter for members
b- Pool walls
c- Tunnels
d- Curve member
17- When OPC & SRC are used?
OPC for superstructure
SRC for substructure or for member exposed to soil
18- Density of cement.
1440 kg/m3
19- Density of concrete
2500 kg/m3
20- Definition of concrete durability.
Capability of concrete to resist weathering condition like chloride, chemical attack, and
abrasion
21- Till when the curing should continue?
Till minimum 7 days till the concrete reach 70% of its strength
22- Refer to sampling test in BS 12350-1;2009. Standard term “increment” Is
defined as:
Quantity of concrete taken by single operation of a scoop or similar devices
23- After demolding of cubes, cubes shall be cured immediately before testing in
water at temperature of chamber:
20+- 2 at humidity larger than 95%
24- The minimum allowable capacity of the measuring container used in air content
test is:
5 liters
25- Refer to flow table test, leveling each layer by tamping lightly done for how
many times?
10 times
26- The flow table test values results are reported to the nearest.
10 mm
27- Slump test is used to measure.
Consistency of concrete
28- Refer to density test, the standard specifies the method for determining the
density of compacted fresh concrete is.
BS-EN-12350-1;2009
29- For temperature Test, concrete containing aggregate size larger than 75mm may
require how much time for transfer of heat from aggregate to mortar?
20 mins
30- What is the maximum % of reinforcement of beam?
4%
31- What is the minimum % of reinforcement for beam as BS 8110-97?
0.8 %
32-Wind load test taken from wind for regular building if height more than?
120 meters
33- Modification factor of PT Slab:
0.5
34- the deflection for beam span is:
5Wl4/384 EI
35- Nominal tensile strength for post tension tendons is:
1860 MPa
36- Density of light weight concrete:
Between 800 to 1800 kg/m3
37- What is the poison ratio of concrete?
0.2
38- what is the poison ration of steel structure
0.3
39- Es of steel structure is:
205000 MPa
40- Es of concrete
30000 Mpa
41- Minimum vertical reinforcement in walls is:
0.04 %
42- Minimum vertical reinforcement of columns is:
1%
43- Mechanical splice (min 50 diameter) may be used after demonstrating that splice
can develop:
125% of the specified yield strength of the bar
44- the maximum deflection for cantilever beam under uniform load is:
Wl4/ 8 EI
46- As per DIN 1048 Standard, water penetration at 28 days test should not exceed
maximum of:
10 mm
47- As per ASTM C 1202 the rapid chloride penetration test at 28 days for RC pile
should not exceed:
1200 Columbus
48- As per ACI 318-4 the maximum allowable elongation in post tension tendons is:
7%
49- maximum spacing for PT tendons as per ACI 318-05 IS:
8 THICKNESS OF SLAB or 5 ft
50- Maximum acceptable settlement for the piles under working load:
8mm
51- the normal consistency of Portland cement is
25.35 %
52- the Modulus of elasticity of normal concrete is
4700 √f’c N/mm2
53- in post tension the maximum number of strands used per tendons is
5
54- For external walls of building whose U value should be 0.52 w/m2*k, the
thickness of polystyrene should be:
60 mm
55- cover for structural members:
a- Columns & beams 30 mm
b- Foundation 50 mm
c- Pile and exposed to soil 70 mm
56- maximum settlement of raft foundation is
50 mm
57- maximum settlement of isolated footing is
30 mm
58- maximum steel in strap footing is located at?
Top
59- overlap of steel of continues beam done at:
Mid third span at bottom and middle span for top
60- The concrete used for structural purpose shall have compressive strength not
less than:
Minimum Fcu 35 N.mm2 for post tension minimum Fcu 40 N/mm2
61- shear & moment diagram
62- design lifetime of structure:
63- Concrete combination design:
64- Reinforcement details for PT slabs
65- precast slab connection details:
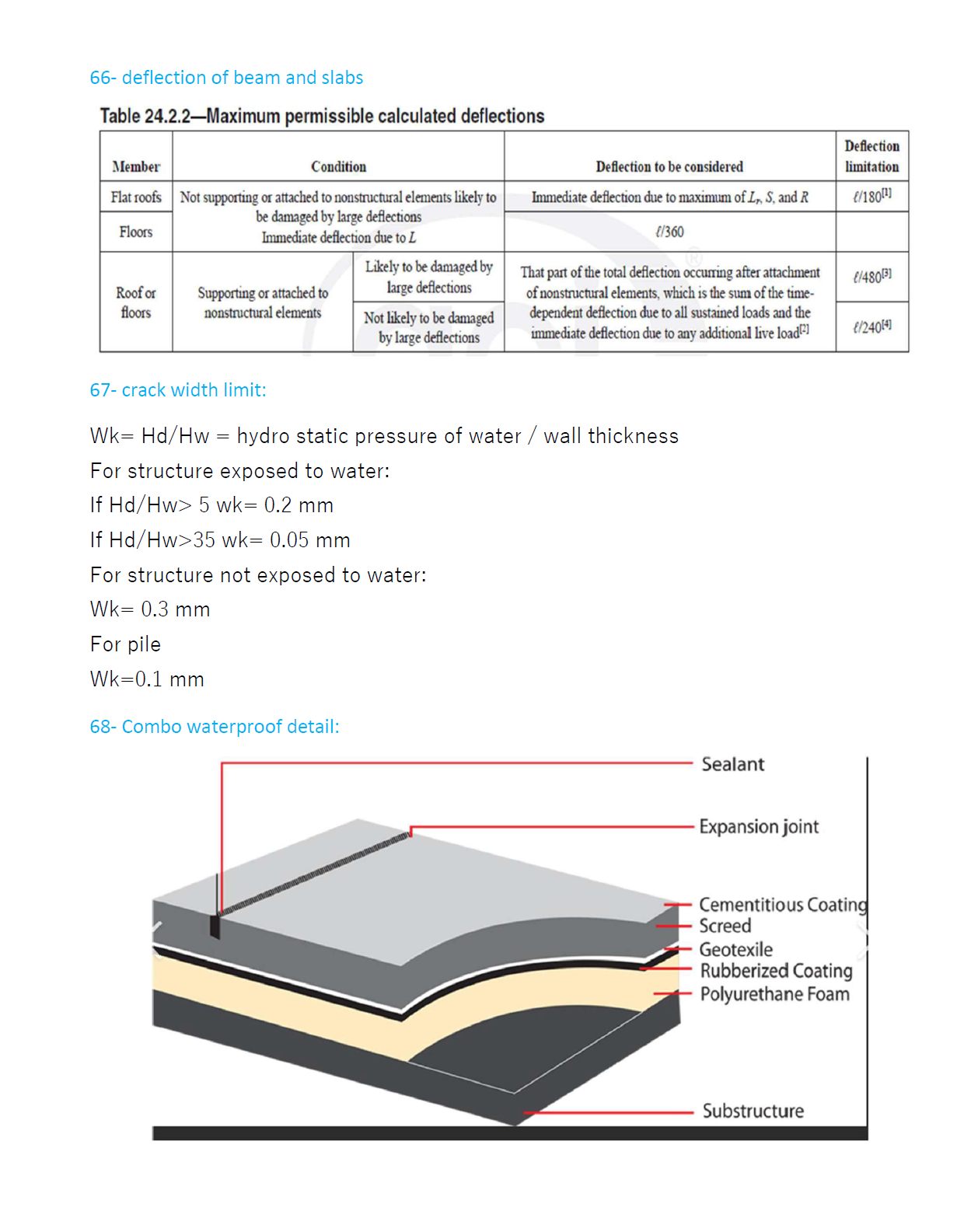
66- deflection of beam and slabs
67- crack width limit:
Wk= Hd/Hw = hydro static pressure of water / wall thickness
For structure exposed to water:
If Hd/Hw> 5 wk= 0.2 mm
If Hd/Hw>35 wk= 0.05 mm
For structure not exposed to water:
Wk= 0.3 mm
For pile
Wk=0.1 mm
68- Combo waterproof detail:


Comments ()