In the dynamic world of project management, keeping a project on track involves meticulous planning and regular performance evaluations. Earned Value Management (EVM) is a robust methodology that integrates project scope, schedule, and cost variables to give project managers a comprehensive view of project performance. In this article, we delve into the essentials of EVM and explore the insights offered by project management tools, using data from a sample project schedule and cash flow analysis.
What is Earned Value Management (EVM)?
Earned Value Management is a project management technique used to measure project performance against the project plan. EVM allows project managers to calculate:
- Planned Value (PV): The budgeted cost for work scheduled to be completed by a certain date.
- Actual Cost (AC): The actual cost incurred for work completed by a certain date.
- Earned Value (EV): The budgeted cost for work actually completed by a certain date.
Using these metrics, project managers can derive essential performance indicators such as:
- Cost Variance (CV): CV=EV−ACCV = EV - ACCV=EV−AC
- Schedule Variance (SV): SV=EV−PVSV = EV - PVSV=EV−PV
- Cost Performance Index (CPI): CPI=EVACCPI = \frac{EV}{AC}CPI=ACEV
- Schedule Performance Index (SPI): SPI=EVPVSPI = \frac{EV}{PV}SPI=PVEV
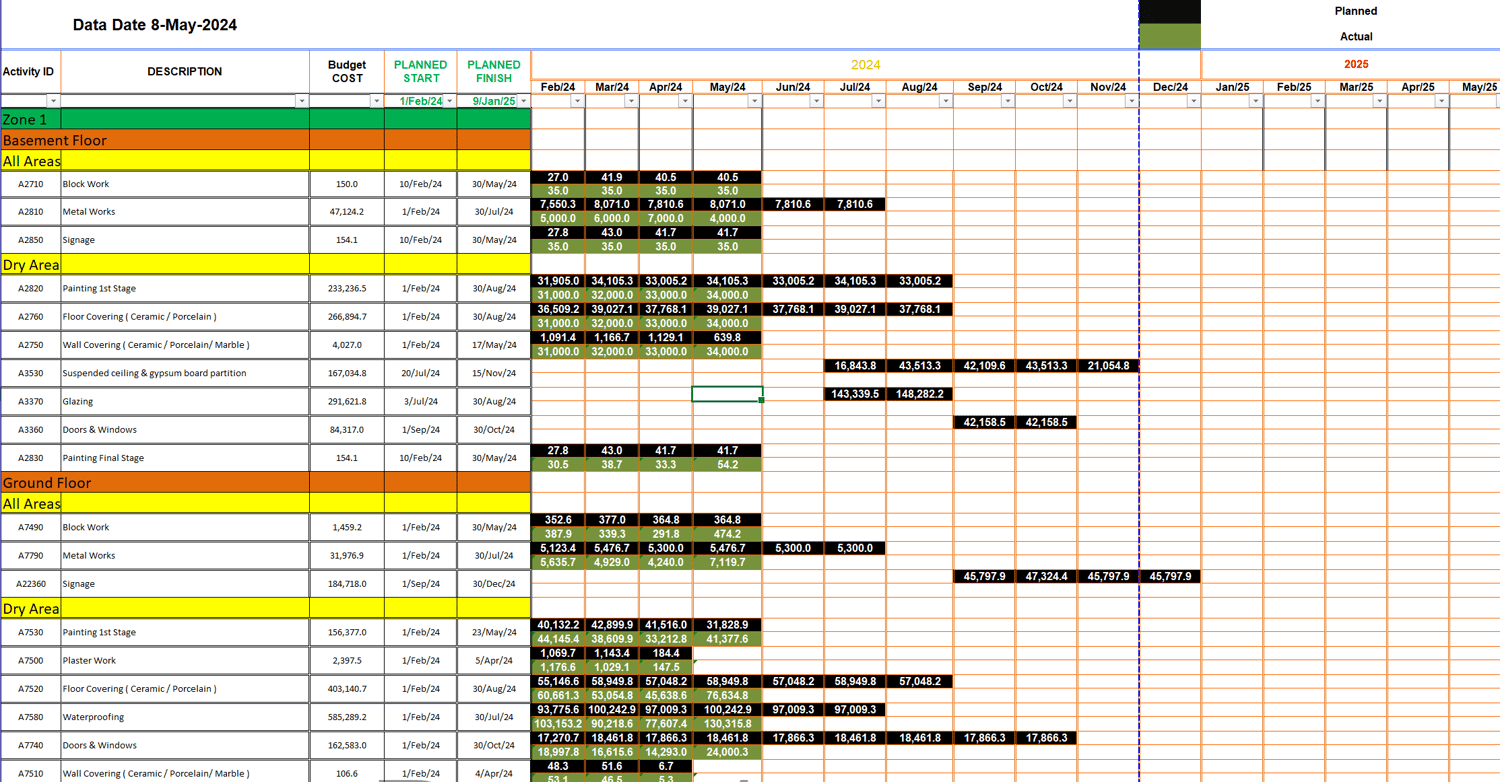
Project Schedule Analysis: The "Bar Chart" Sheet
The "Bar Chart" sheet in our sample Excel file is crucial for visualizing project timelines and monitoring progress. It includes columns such as:
- Activity ID: Unique identifiers for project tasks.
- Description: Detailed descriptions of each activity.
- % Completed: The percentage of work completed for each task.
- Budget Cost: The planned budget for each task.
- Planned Start and Finish Dates: The scheduled start and finish dates for each activity.
- Construction Percentage and Monthly Data: Detailed monthly construction progress and associated costs.
Analyzing this data helps project managers track whether tasks are being completed on time and within budget. For instance, by comparing the "% Completed" with the "Planned Start and Finish Dates," managers can quickly identify schedule variances.
Cash Flow Management: The "Cash Flow" Sheet
Effective cash flow management is critical for project success. The "Cash Flow" sheet provides insights into the financial health of the project, highlighting both planned and actual expenditures over time. Key components include:
- Planned vs. Actual Cash Flow: A comparison of expected and actual cash disbursements, helping to identify discrepancies.
- Monthly Breakdown: Detailed monthly cash flow data to monitor trends and make informed financial decisions.
By regularly reviewing this data, project managers can ensure that financial resources are being utilized efficiently and can adjust plans as necessary to mitigate risks.
Leveraging EVM for Project Success
Implementing Earned Value Management allows project managers to:
- Track Performance Accurately: EVM offers a quantifiable approach to measure project performance against the plan.
- Identify Issues Early: By monitoring CV and SV, managers can detect deviations from the plan early and take corrective actions.
- Enhance Decision-Making: Accurate performance data supports better decision-making and more effective project control.
Conclusion
Earned Value Management is an indispensable tool in the arsenal of project managers. By integrating project scope, schedule, and cost variables, EVM provides a comprehensive view of project performance, enabling timely interventions and informed decision-making. Tools like detailed project schedules and cash flow analyses are essential for applying EVM effectively, ensuring projects are completed on time and within budget.
By embracing EVM and leveraging detailed project management data, organizations can significantly improve their project outcomes and achieve greater success in their endeavors.


Comments ()